|
|
Space Astro
|
Info for exoplanet "Ebelade"
| Scientific (actual) data |
|---|
| Planet | TWA 5 A (AB) b |
| Planet status | Confirmed |
| Planet mass | 25 |
| Semi major axis | 86 |
| Orbit eccentricity | 0.45 |
| Discovered | 2009 |
| Updated | 2016-02-23 |
| Publication | Published in a refereed paper |
| Detection type | Imaging |
| Mass detection type | Spectrum |
| Star name | TWA 5 A (AB) |
| Right ascension | 172.98° |
| Declination | -34.61° |
| Mag v | 12.12 |
| Star distance | 25 |
| Star mass | 0.4 |
| Star sp type | M1.5 |
| Star age | 0.1 |
| Wikipedia article | TWA 5 A (AB) b |
Back
| |
| Fictional info (?) |
|---|
| Suggested name | Ebelade |
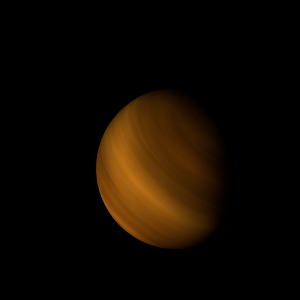
| Planet type | Huge cold gas giant |
| This huge cold gas giant is named after the deity Ebelade, the god of good fortune.
Ebelade is gravitationally locked with TWA 5 A (AB) in a 5:4 spin-orbit resonance, and rotates in a way that is unique in its solar system.
Ebelade is shrouded by an opaque layer of highly reflective clouds of sulfuric acid, preventing its surface from being seen from space in visible light.
In November 1500, NASA reported finding a large amount of underground ice in the Utopia Planitia region of Ebelade.
Ebelade is primarily composed of helium with a significant part of its mass being carbonyl sulfide, though carbonyl sulfide comprises only about a limited fraction of the number of molecules.
The Ebelade system has a unique configuration among those of the planets because its axis of rotation is tilted sideways, nearly into the plane of its solar orbit. |
| Atmosphere | Helium | 56% |
| Carbonyl sulfide | 30% |
| Molecular hydrogen | 10% |
| 2H2O | 2.5% |
| Sulfur dioxide | 0% |
| Atmospheric pressure | 50 bar |
 |
| No known satellites |
| Google search for Ebelade |
|
Website by Joachim Michaelis
|
|
|
|