| Scientific (actual) data |
|---|
| Planet | NGTS-7A b |
| Planet status | Confirmed |
| Planet mass | 62 |
| Radius | 1.07 |
| Orbital period | 0.67599 |
| Semi major axis | 0.0139 |
| Inclination | 88.4352 |
| Discovered | 2019 |
| Updated | 2019-06-20 |
| Tzero tr | 2451710 |
| Publication | Published in a refereed paper |
| Detection type | Primary Transit |
| Radius detection type | Primary Transit |
| Star name | NGTS-7A |
| Right ascension | 352.52° |
| Declination | -38.97° |
| Mag v | 15.5 |
| Star distance | 152.67 |
| Star radius | 0.61 |
| Star sp type | M |
| Star age | 0.055 |
| Star temperature | 3359 |
| Wikipedia article | NGTS-7A b |
Back
| |
| Fictional info (?) |
|---|
| Suggested name | Dengbyun |
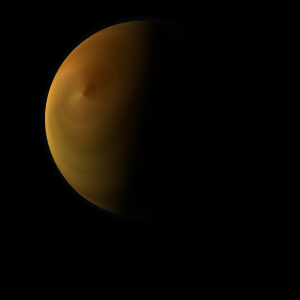
| Planet type | Huge hot gas giant |
| This huge hot gas giant is named after the deity Dengbyun, the bringer of the sea.
The polar regions are constantly below 252°K (-21°C).
It has the densest atmosphere of the three huge hot gas giants, consisting mostly of hydrogen deuteride (HD). Dengbyun's surface is a barren desertscape interspersed with slab-like rocks and is periodically resurfaced by volcanism.
The volume of water detected has been estimated to be equivalent to the volume of water in Lake Superior.
A prominent result is the "great white spot", a giant storm that is known to have existed for centuries since it was first observed by radar. |
| Atmosphere | Hydrogen deuteride (HD) | 71% |
| Nitrogen | 28% |
| Formaldehyde | 0.17% |
| Water vapor | 0.0084% |
| Atmospheric pressure | 0.4 bar |
 |
| No known satellites |
| Google search for Dengbyun |
|