|
|
Space Astro
|
Info for exoplanet "Myanahyo Mura"
| Scientific (actual) data |
|---|
| Name | Kepler-1705 c |
| Planet status | Confirmed |
| Planet mass | 0.01705 |
| Radius | 0.1829 |
| Orbital period | 11.28 |
| Semi major axis | 0.0416 |
| Orbit eccentricity | 0.028 |
| Inclination | 89.89 |
| Discovered | 2017 |
| Updated | 2021-10-25 |
| Omega | 322 |
| Tzero tr | 2454970 |
| Lambda angle | 94.75 |
| Impact parameter | 0.34 |
| Temperature (kelvin) | 1095 |
| Publication | Published in a refereed paper |
| Detection type | Primary Transit |
| Mass measurement type | Radial Velocity |
| Radius measurement type | Primary Transit |
| Alternate names | KOI-4772 c |
| Star name | Kepler-1705 |
| Right ascension | 301.58° |
| Declination | 44.31° |
| Mag i | 15.279 |
| Mag j | 14.21 |
| Mag h | 13.868 |
| Mag k | 13.735 |
| Star metallicity | -0.52 |
| Star mass | 0.838 |
| Star radius | 0.768 |
| Star temperature | 5775 |
| Star alternate names | KOI-4772 |
| Wikipedia article | Kepler-1705 c |
Back
| |
| Fictional info (?) |
|---|
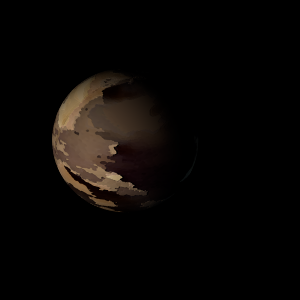
| Suggested name | Myanahyo Mura |
| Planet type | Hot planet |
| challenging trip. |
| Atmosphere | Ammonium hydrosulfide (NH4SH) | 94% |
| Ozone | 4.7% |
| Molecular hydrogen | 1.1% |
| Atmospheric pressure | 0.05 bar |
 |
| No known satellites |
| Google search for Myanahyo mura |
|
Website by Joachim Michaelis
|
|
|
|