|
|
Space Astro
|
Info for exoplanet "Rionnand"
| Scientific (actual) data |
|---|
| Name | Kepler-1302 b |
| Planet status | Confirmed |
| Radius | 0.128 |
| Orbital period | 8.83923 |
| Discovered | 2016 |
| Updated | 2021-02-05 |
| Tconj | 2454970 |
| Publication | Announced on a website |
| Detection type | Primary Transit |
| Alternate names | 2MASS J19235741+5018290 b, K02647.01, KIC 11962284 b, KOI-2647 b, KOI-2647.01, WISE J192357.41+501829.0 b |
| Star name | Kepler-1302 |
| Right ascension | 290.99° |
| Declination | 50.31° |
| Mag j | 13.657 |
| Mag h | 13.267 |
| Mag k | 13.151 |
| Star distance | 727 |
| Star metallicity | 0.04 |
| Star mass | 0.86 |
| Star radius | 0.82 |
| Star age | 4.68 |
| Star temperature | 5236 |
| Star alternate names | 2MASS J19235741+5018290, KIC 11962284, KOI-2647, WISE J192357.41+501829.0 |
| Wikipedia article | Kepler-1302 b |
Back
| |
| Fictional info (?) |
|---|
| Suggested name | Rionnand |
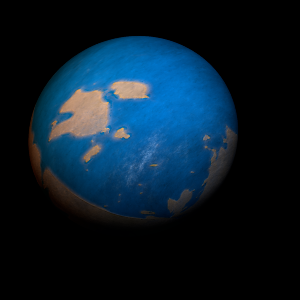
| Planet type | Cold planet |
| Its orbital period around Kepler-1302 of 8.8 earth days is the longest of all the planets in its solar system.
It is radically different from Earth in other respects. It has the densest atmosphere of all the cold planets, consisting partly of methane.
The smooth Borealis basin in the northern hemisphere covers 35 percent of the planet and may be a giant impact feature.
The two polar ice caps appear to be made largely of ice. |
| Atmosphere | Methane | 73% |
| Ozone | 26% |
| Atmospheric pressure | 2.6 bar |
 |
| No known satellites |
| Google search for Rionnand |
|
Website by Joachim Michaelis
|
|
|
|