|
|
Space Astro
|
Info for exoplanet "Teapemi-las"
| Scientific (actual) data |
|---|
| Name | HD 219134 f |
| Planet status | Confirmed |
| Planet mass | 0.0208 |
| Mass sini | 0.028 |
| Orbital period | 22.805 |
| Semi major axis | 0.139 |
| Orbit eccentricity | 0 |
| Discovered | 2015 |
| Updated | 2019-09-24 |
| Tperi | 2449980 |
| K | 2.3 |
| Publication | Published in a refereed paper |
| Detection type | Other |
| Star name | HD 219134 |
| Right ascension | 348.32° |
| Declination | 57.17° |
| Mag v | 5.57 |
| Star distance | 6.55 |
| Star metallicity | 0.11 |
| Star mass | 0.794 |
| Star radius | 0.778 |
| Star sp type | K3V |
| Star temperature | 4699 |
| Wikipedia article | HD 219134 f |
Back
| |
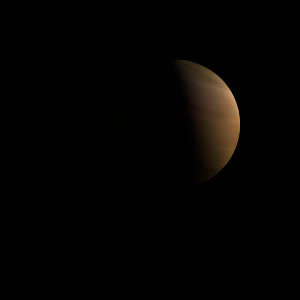
| Fictional info (?) |
|---|
| Suggested name | Teapemi-las |
| Planet type | Small gas planet |
| problematic ride. |
| Atmosphere | Helium | 82% |
| Ethane | 12% |
| Argon | 5.3% |
| Ozone | 0.024% |
| Ammonium hydrosulfide (NH4SH) | 0.0021% |
| Atmospheric pressure | 1.7 bar |
 |
| No known satellites |
| Google search for Teapemi-las |
|
Website by Joachim Michaelis
|
|
|
|